The dog stifle joint, often mistaken for a knee, is a complex and crucial part of a dog’s hind leg anatomy. Understanding the dog stifle anatomy is essential for every dog owner, particularly those with breeds prone to stifle issues. Knowing how this joint works can help you recognize potential problems early on, provide better care, and ensure your furry friend enjoys a healthy, active life. Let’s delve into the intricate world of the dog stifle.
The Key Components of a Dog’s Stifle
The dog stifle is comprised of several key components that work together to facilitate movement and stability. These components include:
- Femur: The thigh bone, the largest bone in a dog’s body.
- Tibia: The shin bone, one of the two bones in the lower leg.
- Fibula: The smaller bone in the lower leg.
- Patella: The kneecap, a small bone that sits in front of the stifle joint.
- Menisci: C-shaped pieces of cartilage that act as shock absorbers between the femur and tibia.
- Cruciate Ligaments: These ligaments (anterior and posterior) connect the femur and tibia, providing stability to the joint.
- Collateral Ligaments: These ligaments provide additional support to the sides of the joint.
Common Stifle Injuries in Dogs
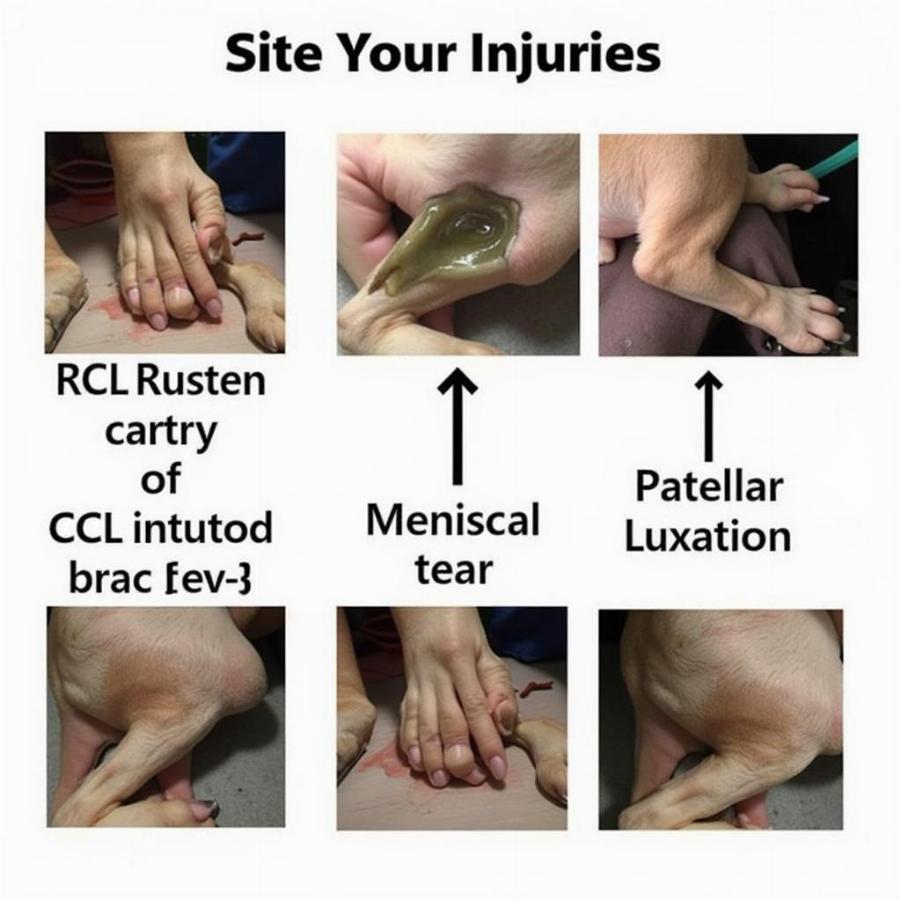
Unfortunately, the stifle joint is susceptible to a variety of injuries, especially in active or larger breeds. Some common stifle injuries include:
- Cranial Cruciate Ligament (CCL) Rupture: This is the most common stifle injury in dogs, similar to an ACL tear in humans. anatomy dog knee joint provides more detailed information on this specific injury.
- Meniscal Tears: These often occur in conjunction with CCL ruptures.
- Patellar Luxation: This involves the kneecap slipping out of its normal position.
- Arthritis: Degenerative joint disease that can affect the stifle, causing pain and stiffness.
Why is Understanding Dog Stifle Anatomy Important?
Understanding the dog stifle anatomy allows you to:
- Recognize early signs of injury: Limping, stiffness, and swelling are common indicators of stifle problems.
- Communicate effectively with your veterinarian: Knowing the terminology associated with the stifle allows for clearer communication during diagnosis and treatment.
- Make informed decisions about your dog’s care: Understanding the anatomy helps you understand the different treatment options available and their potential impact on your dog.
 Các vấn đề khớp gối ở chó
Các vấn đề khớp gối ở chó
How to Keep Your Dog’s Stifle Healthy
Maintaining a healthy weight, providing regular exercise, and using joint supplements can help support your dog’s stifle health. You can learn more about the muscles supporting the stifle in muscles in dog leg. Additionally, understanding the overall anatomy of the hind leg can be beneficial. You can explore this topic further in anatomy of dog hind leg.
Does My Dog Even Have Knees?
This is a common question among dog owners. Technically, dogs don’t have knees in the same way humans do. The joint often referred to as the knee is actually the stifle. For a more detailed explanation, check out do dogs have knees. Understanding the difference is important for accurate communication with your vet. The tibia, a key bone in the stifle joint, is discussed further in tibia in dogs.
Conclusion
Understanding your dog’s stifle anatomy is a cornerstone of responsible pet ownership. By familiarizing yourself with the structure and function of this vital joint, you can play a proactive role in preventing injuries and ensuring your dog’s long-term health and mobility.
FAQ
- What is the most common stifle injury in dogs? Cranial Cruciate Ligament (CCL) rupture.
- What are the signs of a stifle injury? Limping, swelling, stiffness, and pain.
- How can I prevent stifle injuries in my dog? Maintain a healthy weight, provide regular exercise, and consider joint supplements.
- What is the difference between a stifle and a knee? The stifle is the equivalent of the human knee in dogs.
- What are the treatment options for stifle injuries? Treatment options vary depending on the severity and type of injury, ranging from conservative management to surgery.
Dr. Emily Carter, DVM, a renowned veterinary orthopedic surgeon, emphasizes, “Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for successful management of stifle injuries in dogs.” Another expert, Dr. Sarah Miller, PhD in Animal Physiology, adds, “A thorough understanding of the dog’s stifle anatomy is paramount for both owners and veterinarians to effectively address and prevent stifle-related issues.”
Beaut Dogs is your trusted source for comprehensive and reliable information on all aspects of dog care, from breed selection to health and wellness. For further assistance and personalized advice regarding your dog’s stifle health, please contact us via Email at [email protected]. Beaut Dogs is dedicated to providing expert guidance and support to help you ensure the well-being of your beloved canine companion. Visit us at https://beautdogs.com today to explore our wealth of resources and discover everything you need to know about caring for your furry friend.