If you’ve ever seen your furry friend limping or favoring their front leg, you know how distressing it can be. A dog front leg injury can range from minor sprains to serious fractures, and understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for any responsible dog owner. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of dog front leg injuries, equipping you with the knowledge to provide the best possible care for your canine companion.
Common Causes of Front Leg Injuries in Dogs
Dogs are naturally active and playful creatures, and this exuberance can sometimes lead to mishaps. Here are some of the most prevalent causes of front leg injuries in dogs:
- Traumatic injuries: Just like humans, dogs can experience sudden injuries from falls, car accidents, or being stepped on.
- Overexertion: Engaging in strenuous activities without proper conditioning, particularly in athletic or working breeds, can strain muscles and tendons.
- Degenerative diseases: Conditions like arthritis and hip dysplasia can weaken joints and ligaments, making them more susceptible to injuries.
- Congenital conditions: Some breeds may be predisposed to certain joint or bone conditions, increasing their risk of front leg problems.
Identifying a Front Leg Injury: Signs to Watch For
Early detection is key to effective treatment. Keep a close eye on your canine companion for these telltale signs of a front leg injury:
- Limping: This is often the most obvious symptom, indicating pain or discomfort.
- Holding the leg up: If your dog refuses to put weight on the injured leg, it’s a clear sign of a problem.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the injured area is a natural response to injury.
- Pain or tenderness: Whining, yelping, or flinching when the injured area is touched.
- Changes in gait: You may notice your dog walking differently, shifting their weight, or having difficulty moving.
Diagnosing the Problem: What to Expect at the Vet
If you suspect your dog has a front leg injury, a visit to the veterinarian is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. The vet will likely perform a physical examination, checking for:
- Range of motion: To assess joint flexibility and identify any stiffness or pain.
- Swelling and tenderness: Palpating the leg to pinpoint the location and severity of the injury.
- Neurological function: Testing reflexes and responses to rule out nerve damage.
In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be necessary, including:
- X-rays: To visualize bones and detect fractures, dislocations, or bone diseases.
- MRI or CT scan: These imaging techniques provide detailed views of soft tissues like ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
Treatment Options: From Rest to Surgery
The treatment plan for a dog’s front leg injury will vary greatly depending on the severity and type of injury.
Conservative Management:
- Rest: Restricting your dog’s activity is crucial for healing, especially in the initial stages.
- Cold therapy: Applying ice packs can reduce inflammation and numb the area.
- Compression: Bandaging or wrapping the injured leg can help minimize swelling.
- Medications: Pain relievers, anti-inflammatories, or antibiotics may be prescribed.
Surgical Intervention:
- Fracture repair: Surgical procedures may be needed to stabilize broken bones using pins, plates, or screws.
- Ligament or tendon repair: For severe tears, surgery can help reconnect and stabilize damaged tissues.
- Joint replacement: In cases of severe joint disease or damage, a joint replacement surgery may be recommended.
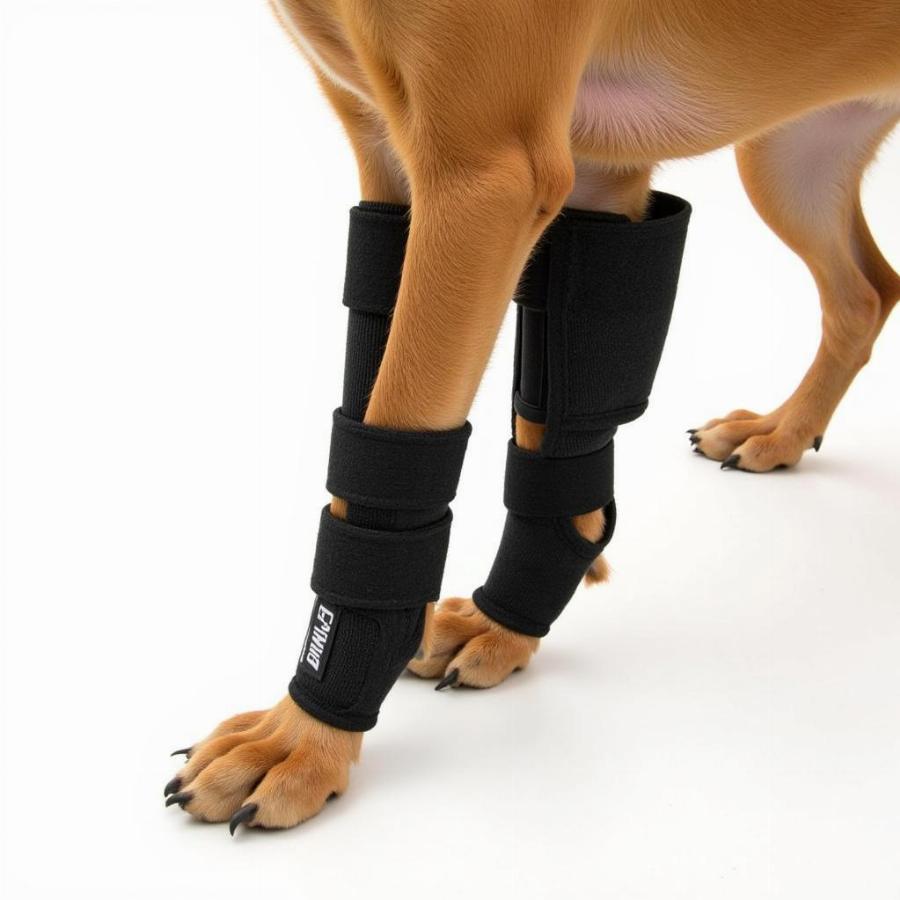 Dog with a Front Leg Brace
Dog with a Front Leg Brace
Recovery and Rehabilitation: Getting Your Dog Back on Their Paws
Recovery from a front leg injury is a journey that requires patience, dedication, and a tailored rehabilitation plan.
- Physical therapy: Exercises designed to strengthen muscles, improve range of motion, and restore mobility.
- Hydrotherapy: Water therapy can be incredibly beneficial, providing low-impact exercise and support for injured joints.
- Assistive devices: Braces, slings, or harnesses can provide support and stability during the healing process.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential to reduce stress on injured joints.
Preventing Future Injuries: Proactive Steps for Happy Paws
While not all injuries are preventable, taking proactive measures can significantly reduce your dog’s risk:
- Controlled exercise: Provide regular, moderate exercise to maintain muscle strength and joint health.
- Warm-up and cool-down: Just like with human athletes, warming up before strenuous activity and cooling down afterward can help prevent injuries.
- Weight management: Obesity puts extra strain on joints, increasing the risk of injuries.
- Environmental safety: Ensure your home and yard are free of hazards that could cause falls or other accidents.
FAQs About Dog Front Leg Injuries
How long does it take for a dog’s front leg to heal?
Healing time varies greatly depending on the severity and type of injury. It can range from a few weeks for minor sprains to several months for fractures or surgeries.
What should I do if my dog suddenly starts limping?
If you notice sudden limping, restrict your dog’s activity and observe them closely. If the limping persists or worsens, schedule a veterinary appointment promptly.
Can I treat my dog’s front leg injury at home?
It’s crucial to consult with a veterinarian for diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Home remedies may be appropriate for minor injuries, but professional guidance is essential.
How can I make my dog comfortable during recovery?
Provide a comfortable and supportive resting area. Consider orthopedic beds, blankets, and toys to keep your dog entertained and comfortable.
When can my dog resume normal activity after a front leg injury?
Follow your veterinarian’s instructions regarding activity restrictions. Gradually increase your dog’s activity level as advised to avoid re-injury.
What are the signs of a serious front leg injury?
Signs of a serious injury include intense pain, inability to bear weight on the leg, dangling or misshapen limbs, and open wounds.
How can I prevent my dog from injuring their front leg again?
Follow the preventive measures outlined earlier, including controlled exercise, weight management, and environmental safety.
Need More Help? Contact Beaut Dogs
Dealing with a dog front leg injury can be a challenging experience for both you and your furry companion. Remember, early detection and prompt veterinary care are paramount. By following your veterinarian’s guidance and providing proper care and rehabilitation, you can help your dog recover fully and regain their mobility. For more insightful information on dog health, care, and well-being, visit Beaut Dogs at https://beautdogs.com. When you need expert advice and support, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at [email protected]. We’re here to help you navigate the world of dog ownership with confidence and compassion.