Have you ever wondered, while watching a documentary about grizzly bears or playing fetch with your furry best friend, “are bears related to dogs?” The answer might surprise you. While seemingly different on the surface – a massive, lumbering bear compared to a playful pup – these creatures share a deeper connection rooted in their evolutionary history.
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of canine ancestry and explore the branches of the evolutionary tree that link bears and dogs.
A Shared Ancestry: Tracing Back to the Carnivora Order
To understand the relationship between bears and dogs, we need to go back millions of years. Both animals belong to the order Carnivora, a diverse group that also includes cats, weasels, seals, and even walruses. This means they share a common ancestor way back in time – a creature that possessed characteristics we now associate with carnivores.
Caniformia: The Key to the Connection
Within the Carnivora order, bears and dogs belong to a suborder called Caniformia – the “dog-like” carnivores. This group, which branched off around 42 million years ago, also includes wolves, foxes, raccoons, and even seals. The Caniformia are characterized by certain physical traits, like having non-retractable claws and a longer snout compared to their feline counterparts.
Unpacking the Family Tree: Ursidae vs. Canidae
Here’s where the family tree branches off. Bears belong to the family Ursidae, while dogs belong to Canidae. While these families diverged millions of years ago, their shared Caniformia ancestry is evident in their physical characteristics and some behavioral traits.
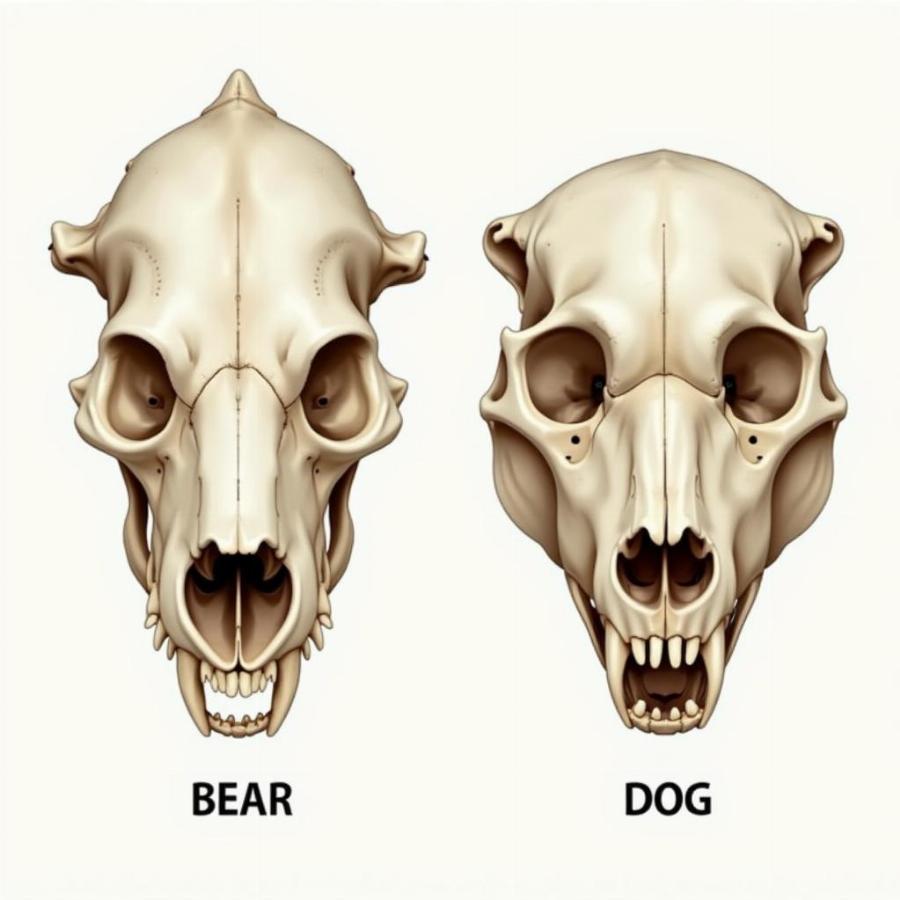 Comparison of Bear and Dog Skulls
Comparison of Bear and Dog Skulls
“Despite their differences in size and appearance, the skeletal structures of bears and dogs reveal striking similarities, particularly in their teeth and jaw structure, indicative of their shared carnivorous ancestry,” explains Dr. Sarah Williams, a paleontologist specializing in Caniformia evolution.
Similarities Beyond the Surface
The bear-dog connection isn’t limited to just bones and fossils. Both animals exhibit surprising similarities in their:
- Keen sense of smell: Bears and dogs possess an incredibly powerful sense of smell, far superior to humans. This shared trait is crucial for hunting, navigating their surroundings, and even communicating with each other.
- Dietary similarities: While bears are omnivores and dogs are generally considered carnivores, both demonstrate a flexible diet and opportunistic feeding behaviors.
- Social structures: Although there are solitary bear species, many live in social groups with complex hierarchies, much like wild dog packs.
Bears and Dogs: A Connection Through Time
Understanding the evolutionary connection between bears and dogs gives us a new appreciation for the diversity and interconnectedness of the animal kingdom. While separated by millions of years of evolution, the remnants of their shared ancestry are etched in their bones, senses, and even behaviors.
FAQs
Q: Are dogs more closely related to wolves or bears?
A: Dogs are more closely related to wolves, as they both belong to the Canidae family.
Q: Do bears and dogs share any common diseases?
A: While rare, there have been instances of diseases jumping between bears and dogs, highlighting their biological connections.
Q: Why do bears and dogs both have such a good sense of smell?
A: Their shared Caniformia ancestry favored the development of a strong sense of smell for hunting and survival.
Q: Can dogs and bears interbreed?
A: No, due to millions of years of evolutionary divergence, bears and dogs cannot interbreed.
Want to Learn More About the Canine World?
Beaut Dogs is your ultimate destination for everything dog-related! We offer trusted, informative, and engaging content about the world of dogs. From breed information to care guides, we’ve got you covered.
For personalized advice and answers to your specific dog-related queries, reach out to our experts at [email protected]. Beaut Dogs – your trusted companion in the journey of dog ownership.