Histiocytoma cytology in dogs is a common topic of concern for pet owners. These small, button-like skin growths often appear suddenly and can be alarming. This article will delve into the details of histiocytoma cytology in dogs, offering you a comprehensive understanding of this typically benign skin tumor. We’ll cover what histiocytomas are, how they’re diagnosed using cytology, and what treatment options are available.
What is a Histiocytoma in Dogs?
Histiocytomas are benign skin tumors that arise from Langerhans cells, a type of immune cell residing in the skin. They’re most commonly found in young dogs, typically under three years of age. These growths appear as raised, firm, hairless nodules, often reddish-pink in color. While they can occur anywhere on the body, they are frequently seen on the head, legs, ears, and face.
Diagnosing Histiocytoma with Cytology
Cytology is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying histiocytomas. This procedure involves collecting cells from the tumor using a fine-needle aspirate. The collected sample is then examined under a microscope to determine the cell types present. In the case of a histiocytoma, the cytology will reveal a characteristic population of Langerhans cells. This helps differentiate histiocytomas from other skin growths, such as mast cell tumors or other cancerous masses.
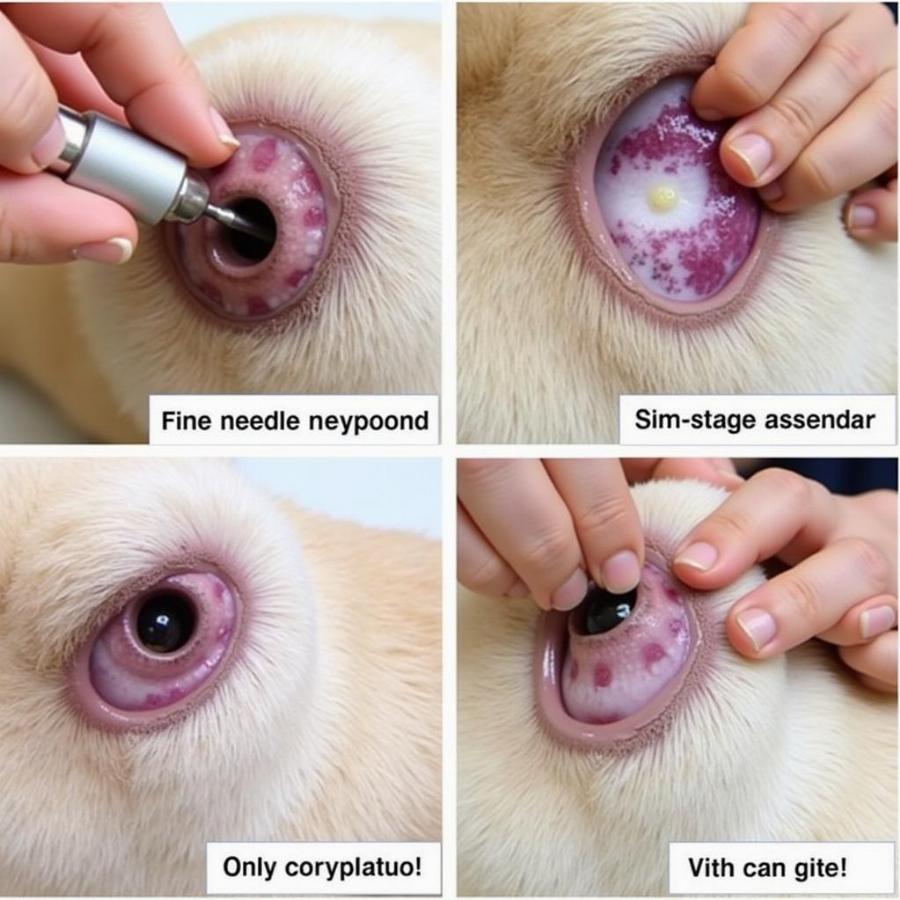 Quy trình lấy mẫu cytology cho histiocytoma ở chó
Quy trình lấy mẫu cytology cho histiocytoma ở chó
Histiocytoma Treatment Options
Many histiocytomas regress spontaneously, meaning they shrink and disappear on their own without any treatment, usually within 2-3 months. This is a defining characteristic of histiocytomas. However, if a histiocytoma is causing discomfort, interfering with normal function, or grows rapidly, surgical removal may be considered. In rare cases, if a histiocytoma doesn’t regress on its own and continues to grow, biopsy and further investigation may be recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions about Histiocytoma Cytology in Dogs
What does a histiocytoma look like on a dog? Histiocytomas typically appear as raised, red, button-like growths on the skin.
Are histiocytomas painful for dogs? Histiocytomas are usually not painful, though they can become irritated if the dog scratches or licks them excessively.
How is histiocytoma cytology performed? A fine needle is inserted into the tumor to collect cells, which are then examined under a microscope.
How long does it take for a histiocytoma to go away? Most histiocytomas regress spontaneously within 2-3 months.
What if my dog’s histiocytoma doesn’t go away? If the histiocytoma doesn’t regress, consult with your veterinarian for further evaluation and potential treatment options.
Can histiocytomas come back after they disappear? Recurrence is rare.
Are histiocytomas contagious to humans or other pets? No, histiocytomas are not contagious.
Conclusion
Histiocytoma cytology is a valuable diagnostic method for confirming the presence of these common skin tumors in dogs. Understanding the nature of these growths, their diagnosis, and the typical course of spontaneous regression can help alleviate anxieties for pet owners. If you notice any unusual skin growth on your dog, consult with your veterinarian for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Other questions related to dog health
- What are the common skin problems in dogs?
- How to identify and treat skin allergies in dogs?
- What are the signs of skin cancer in dogs?
Beaut Dogs is your trusted source for all things dog-related. We provide comprehensive and reliable information on dog breeds, health, care, and training. For personalized advice and support, please contact us at Email: [email protected]. Beaut Dogs is here to help you navigate the wonderful world of dog ownership!