Anal gland surgery in dogs, while sometimes necessary, can be a concerning topic for pet owners. This article will delve into the reasons behind this procedure, the process itself, post-operative care, and alternative solutions. Understanding these aspects can help you make informed decisions for your furry friend’s well-being.
Understanding Anal Gland Issues in Dogs
Dogs have two small sacs located on either side of their anus, known as anal glands. These glands produce a foul-smelling fluid that typically expresses naturally during defecation, marking their territory. However, sometimes these glands can become impacted, infected, or even abscessed, requiring veterinary intervention.
Why Anal Gland Surgery Might Be Necessary
While most anal gland problems can be managed with manual expression or medication, surgery becomes necessary in certain situations. These include recurrent impactions, chronic infections, abscesses that don’t respond to other treatments, and tumors of the anal glands. The goal of anal gland surgery is to remove the problematic glands and alleviate your dog’s discomfort.
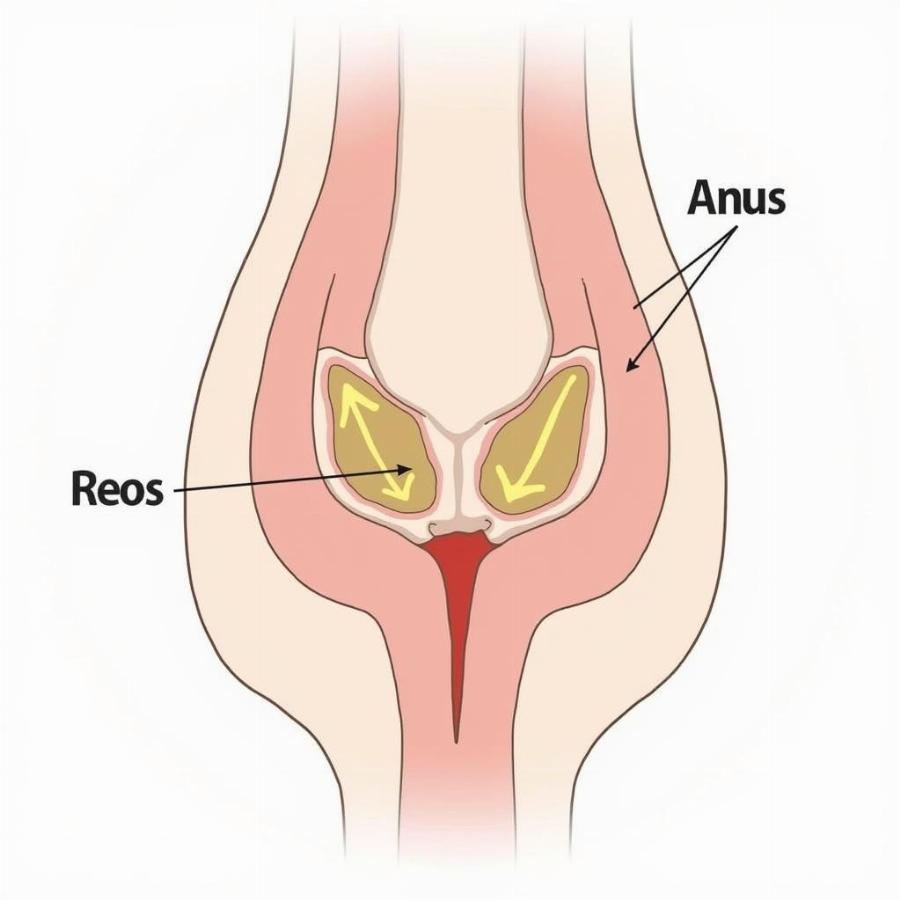 Dog Anal Gland Location
Dog Anal Gland Location
The Anal Gland Surgery Procedure
Anal gland surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The veterinarian will make an incision near the affected gland and carefully remove it. The incision is then closed with sutures. In some cases, a drain may be placed to prevent fluid buildup. The procedure is typically relatively straightforward, but the complexity can vary depending on the specific condition being addressed. For example, a ruptured abscess can require a more extensive procedure.
Post-Operative Care for Anal Gland Surgery
After surgery, your dog will require careful monitoring and at-home care. Pain medication and antibiotics will likely be prescribed to manage discomfort and prevent infection. You will need to keep the incision site clean and dry, and prevent your dog from licking or chewing at the sutures. Elizabethan collars are commonly used to prevent this. Regular checkups with your veterinarian will be necessary to ensure proper healing.
What are the risks of anal gland surgery in dogs?
While generally safe, anal gland surgery does have potential risks, such as infection, fecal incontinence, and nerve damage. It’s important to discuss these risks with your veterinarian to understand the potential complications.
Are there alternatives to anal gland surgery for dogs?
Yes, there are several alternatives to surgery, including manual expression of the glands, dietary changes to increase fiber intake, and medications to reduce inflammation. However, if these treatments are unsuccessful, surgery may be the best option for your dog’s long-term health and comfort. Treatments for anal fistulas may also be an option, depending on the specifics of your dog’s condition. You can read more about this in our article on treatment for anus fistula in dogs.
How can I prevent anal gland problems in my dog?
While not all anal gland problems are preventable, maintaining a healthy weight and a high-fiber diet can help promote regular bowel movements and natural expression of the glands. If you notice your dog scooting their bottom or exhibiting excessive licking around the anal area, consult your veterinarian. Early intervention can often prevent more serious issues from developing. If you are concerned about your dog’s anal area leaking, see our article on dogs bum leaking for more information.
Conclusion
Anal gland surgery in dogs is a viable option for treating persistent and severe anal gland problems. While it’s important to be aware of the risks and post-operative care requirements, the procedure can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life. Discussing all available options with your veterinarian will help you determine the best course of action for your furry companion. Understanding the underlying causes and exploring preventative measures can also contribute to your dog’s long-term anal gland health. You might also find our article on perianal gland adenoma dog helpful.
FAQ
- How long does anal gland surgery take? Typically, the procedure takes about 30-60 minutes.
- What is the recovery time for anal gland surgery in dogs? Most dogs recover within a couple of weeks.
- Is anal gland surgery painful for dogs? Pain medication is administered to manage discomfort.
- Can anal gland problems reoccur after surgery? Recurrence is uncommon, especially with complete removal of the glands.
- How much does anal gland surgery cost? The cost varies depending on the complexity of the case and your location.
- What are the signs of anal gland problems in dogs? Scooting, excessive licking, and a foul odor are common signs.
- Can diet affect anal gland health in dogs? Yes, a high-fiber diet can help regulate bowel movements and gland expression. Just like with glaucoma in dogs, you should always consult your vet before trying any new treatments. You can find information about glaucoma eye drops for dogs on our site.
Further Questions and Related Articles
Are you interested in learning more about other common canine health concerns? You may find our articles on pictures of roundworms in dogs informative.
About Beaut Dogs
Beaut Dogs is your trusted source for all things related to dog care, offering expert advice and valuable resources for every aspect of dog ownership, from breed selection to comprehensive health guides. At Beaut Dogs, https://beautdogs.com, we are passionate about empowering dog lovers with the knowledge they need to provide the best possible care for their beloved canine companions. When you need assistance, contact us at Email: [email protected], and Beaut Dogs will provide you with detailed and accurate answers.